The Critical Role of Ag Commodity Processors
The agricultural industry is a complex and dynamic field that serves as the backbone of global food security. One crucial link in this intricate chain is the ag commodity processor. Ag commodity processing involves several intricate processes and specialized functions that are crucial for transforming raw agricultural products into the consumable goods we rely on every day.
The infographic below provides a comprehensive overview of this essential segment within the agricultural sector, highlighting five core components that drive efficiency and success: Sales & Invoicing, Commodity Purchasing, Commodity Processing, Plant & Equipment Maintenance, and Risk Management.
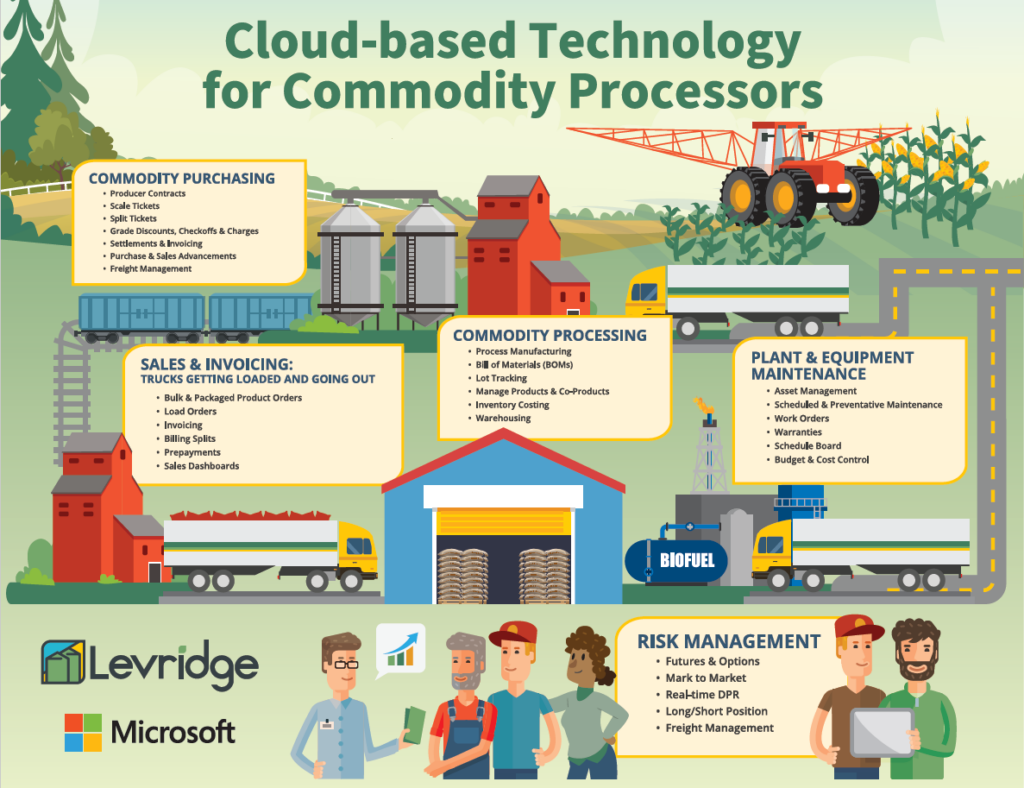
1. Sales & Invoicing
Sales & Invoicing is the linchpin that connects production activities with financial transactions. This function encompasses the management of all commercial exchanges, from negotiating contracts to ensuring timely payments. A streamlined sales and invoicing process is essential for maintaining healthy cash flow and establishing trust with customers.
– Contract Management: Establishing terms and conditions, pricing, and delivery schedules.
– Invoicing: Accurate and timely billing is critical for efficient cash flow management. Automated invoicing systems can reduce errors and improve turnaround times.
– Revenue Recognition: Properly categorizing and recognizing revenue ensures compliance with accounting standards and provides accurate financial reporting.
In the ag commodity processing industry, the ability to handle large volumes of transactions, varying payment terms, and complex pricing structures is particularly vital. A well-implemented sales and invoicing system can significantly enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
2. Commodity Purchasing
Commodity Purchasing is a strategic function that involves sourcing raw materials at optimal prices while ensuring quality and timely delivery. This component directly impacts production costs and overall profitability.
– Supplier Management: Building and maintaining relationships with reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality commodities.
– Market Analysis: Understanding market trends and price fluctuations to make informed purchasing decisions.
– Contract Negotiation: Securing favorable terms for quantity, price, and delivery schedules.
For ag commodity processors, purchasing decisions are often influenced by factors such as seasonality, global supply chains, and geopolitical events. A proactive approach to commodity purchasing helps mitigate risks associated with price volatility and supply shortages.
3. Commodity Processing
Commodity Processing is the core activity where raw agricultural commodities are transformed into finished or semi-finished products. This process involves various stages, each requiring precise control and monitoring to ensure product quality and efficiency.
– Processing Techniques: Different commodities require specific processing techniques, such as milling, refining, or blending. The choice of technology can affect product quality, yield, and cost.
– Quality Control: Implementing stringent quality control measures ensures that the final product meets industry standards and customer expectations.
– Efficiency: Optimizing processing workflows and minimizing waste are crucial for cost control and sustainability.
In the highly competitive ag commodity market, innovation in processing techniques can provide a significant competitive advantage. This could include adopting new technologies for better product yield or exploring eco-friendly processes to meet sustainability goals.
4. Plant & Equipment Maintenance
The smooth operation of processing plants and equipment is vital for maintaining production efficiency and minimizing downtime. Plant & Equipment Maintenance involves regular inspections, repairs, and upgrades to ensure optimal performance and safety.
– Preventive Maintenance: Regular maintenance schedules help prevent unexpected breakdowns and extend the lifespan of equipment.
– Asset Management: Tracking the condition and performance of assets helps in planning replacements and upgrades.
– Safety Compliance: Adhering to safety regulations protects workers and prevents costly fines or legal issues.
In the ag commodity processing industry, equipment downtime can lead to significant financial losses and delays in product delivery. A robust maintenance program is essential to keep operations running smoothly and efficiently.
5. Risk Management
Risk Management in ag commodity processing involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that could impact the business. These risks can range from market volatility and supply chain disruptions to regulatory changes and natural disasters.
– Market Risk: Hedging strategies and market analysis can help manage risks related to price fluctuations of raw materials and finished products.
– Operational Risk: Ensuring that processes and systems are resilient to disruptions, whether from equipment failure, supply chain issues, or workforce challenges.
– Regulatory Compliance: Staying updated with regulations and ensuring compliance to avoid legal penalties and protect the company’s reputation.
Risk management strategies in this sector often involve a mix of financial instruments, insurance, and contingency planning. By proactively managing risks, companies can safeguard their assets and ensure long-term sustainability.
The ag commodity processing industry is a complex ecosystem that relies on the seamless integration of various functions. Sales & Invoicing, Commodity Purchasing, Commodity Processing, Plant & Equipment Maintenance, and Risk Management are all critical components that must work together to drive efficiency and profitability. Understanding and optimizing these functions can lead to better resource utilization, reduced costs, and improved market competitiveness. As the industry continues to evolve, embracing technological advancements and innovative practices in these areas will be key to staying competitive and maintaining long-term success.